Spring:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-Loosely coupled(DI) easy to maintain/test
-predefined templates for JDBC/hibernate etc no need to bother about opening/closing the connection will focus on logic mostly
-Employee(Address address){ } -lOOSELY coupled before creating the object of employee it will checks for the address object
-light weight because of beans/pojo
-Completements J2EE
IOC:
----
-IOC Containers: BeanFactory and ApplicationContext
-Ioc containers are responsible for configuring and creating object ex: BeanFactory.getBean("beancClassId")
DI(loosely coupling):
---------------------
-Instance of Address class is provided by external source such as XML file either by constructor or setter Injections.
class Employee{
Employee(Address address){
this.address=address;
}
-It doesn't depends on other classes
-In bean Configuration every value is string by default If we didn't specify property type (constructor-arg type, value attributes)
-Injections
1.primitives and string
2.Object based
3.Collection Objects List,Set, Map, Props(if both are strings)
List : <list> <value> sample </value> </list>
<list> <ref bean="e1"> </list>
Map: <entry key value>
<entry key-ref value-ref>
-setter injection is better tahn constructor injection ()
-if we use constractor, setter injections then setter injection overrides constractor injection
Autowiring:
-----------
-Inject the object dependency implicitly. It internally uses setter/constructor injection. like B b; setB(); getB();
Facotry:
---------
static factory with own static method of same class
static factory with static method from of another class
non-staic factory: non staic meithod of another class
-configure using factory-miethod and factory-bean attributes
Spring AOP:
----------------
-it cam to avoid repeated code in multiple methods(boiler-plate code)
-@Before @After @Around @AfterThrowing @AfterReturning
Spring JDBC:
-------------
-JdbcTemplate
-NamedParameterJdbcTemplate..etc
-Sping Hbernate: HibernateTemplate
multiThreading:
------------
-sleep(millisecods):thread sleeps for the specified time
- yield() method stops thread for unpredictable time, that depends on thread scheduler
-yield: pause the thread so that other threads can execute
-join: wait the thread to die for specified time
currently running threads to stop executing until the thread it joins with completes its task.
-wait(): releases the lock.
wait() notify () nofifyAll(): are Object class methods we should acquire the lock before using these methods using synchronized blocks/methods
-run() and Start() : to run the thread on any object using object refereces
-Daemon threads are low priority threads which runs intermittently in background for doing garbage collection
-thread priority: max, min
-threadPool: Instead of creating new thread every time for executing tasks, we can create ThreadPool which reuses a fixed number of threads for executing tasks.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Spring-Annotations:
-------------------
@Service
@Repository : Dao
@Component : represents any spring resource/component
@Autowired : to access the bean class in current class
@Transactional :
@Scope : like singleton, prototype, request
Spring MVC Annotations:
@Controller
@RequestMapping : uri(path), method have params like GET, HttpRequest, session..etc.
@PathVariable : at uri_path we can specify like projectname/classlevele_uri/methodlevel_uri/Sample
we can retrive that sample uri as pathvariable like @PathVariable(String Sample)
@RequestParam : like request.getParameter("username") here !RequestParam(String Username)
@ModelAttribute ("formObject")
@SessionAttributes
Spring Security Annotations:
@PreAuthorize
ex:
@Transactional
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
spring bean configurations:
----------------------------------
Model validations
}
--
Destroy(shutDownhook)
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher-servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
1. functional interfaces and lambda expressions
has basctract mehtoda and implemnts of mehtods of ineters face can do
with the lambda expressions we can fileter the collections data with condtions
2. date time api there is no stardr api pro
3.stream api with this we can fileer the collection data
4. forEach can be used to interate the collections data
5. default and static methods implementsation inside interface
6 java 9- private methods in interface
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-Loosely coupled(DI) easy to maintain/test
-predefined templates for JDBC/hibernate etc no need to bother about opening/closing the connection will focus on logic mostly
-Employee(Address address){ } -lOOSELY coupled before creating the object of employee it will checks for the address object
-light weight because of beans/pojo
-Completements J2EE
IOC:
----
-IOC Containers: BeanFactory and ApplicationContext
-Ioc containers are responsible for configuring and creating object ex: BeanFactory.getBean("beancClassId")
DI(loosely coupling):
---------------------
-Instance of Address class is provided by external source such as XML file either by constructor or setter Injections.
class Employee{
Employee(Address address){
this.address=address;
}
-It doesn't depends on other classes
-In bean Configuration every value is string by default If we didn't specify property type (constructor-arg type, value attributes)
-Injections
1.primitives and string
2.Object based
3.Collection Objects List,Set, Map, Props(if both are strings)
List : <list> <value> sample </value> </list>
<list> <ref bean="e1"> </list>
Map: <entry key value>
<entry key-ref value-ref>
-setter injection is better tahn constructor injection ()
-if we use constractor, setter injections then setter injection overrides constractor injection
Autowiring:
-----------
-Inject the object dependency implicitly. It internally uses setter/constructor injection. like B b; setB(); getB();
Facotry:
---------
static factory with own static method of same class
static factory with static method from of another class
non-staic factory: non staic meithod of another class
-configure using factory-miethod and factory-bean attributes
Spring AOP:
----------------
-it cam to avoid repeated code in multiple methods(boiler-plate code)
-@Before @After @Around @AfterThrowing @AfterReturning
Spring JDBC:
-------------
-JdbcTemplate
-NamedParameterJdbcTemplate..etc
-Sping Hbernate: HibernateTemplate
multiThreading:
------------
-sleep(millisecods):thread sleeps for the specified time
- yield() method stops thread for unpredictable time, that depends on thread scheduler
-yield: pause the thread so that other threads can execute
-join: wait the thread to die for specified time
currently running threads to stop executing until the thread it joins with completes its task.
-wait(): releases the lock.
wait() notify () nofifyAll(): are Object class methods we should acquire the lock before using these methods using synchronized blocks/methods
-run() and Start() : to run the thread on any object using object refereces
-Daemon threads are low priority threads which runs intermittently in background for doing garbage collection
-thread priority: max, min
-threadPool: Instead of creating new thread every time for executing tasks, we can create ThreadPool which reuses a fixed number of threads for executing tasks.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Spring-Annotations:
-------------------
@Service
@Repository : Dao
@Component : represents any spring resource/component
@Autowired : to access the bean class in current class
@Transactional :
@Scope : like singleton, prototype, request
Spring MVC Annotations:
@Controller
@RequestMapping : uri(path), method have params like GET, HttpRequest, session..etc.
@PathVariable : at uri_path we can specify like projectname/classlevele_uri/methodlevel_uri/Sample
we can retrive that sample uri as pathvariable like @PathVariable(String Sample)
@RequestParam : like request.getParameter("username") here !RequestParam(String Username)
@ModelAttribute ("formObject")
@SessionAttributes
Spring Security Annotations:
@PreAuthorize
ex:
@Transactional
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
@Required public void setName(String name) {
spring bean configurations:
----------------------------------
<context:annotation-config /><tx:annotation-driven /><context:component-scan base-package="com.howtodoinjava.controller" />
----------------------------------@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String doLogin(@Valid @ModelAttribute("userForm") User userForm, BindingResult result, Map<String, Object> model) { if (result.hasErrors()) { return "LoginForm"; } return "LoginSuccess"; }Model validations
public class User { @NotEmpty @Email private String email; @NotEmpty(message = "Please enter your password.") @Size(min = 6, max = 15, message = "Your password must between 6 and 15 characters")}
--
model.addObject("message", "This page demonstrates how to use Spring security."); return model;
------------------
spring-security.xml:
<user name="admin" password="nimda" authorities="ROLE_ADMIN" />
Spring AOP:------------@Before("businessService()") public void doBeforeTask(){ ... } @After("businessService()") public void doAfterTask(){ ... } @AfterReturning(pointcut = "businessService()", returning = "retVal") public void doAfterReturnningTask(Object retVal) { // you can intercept retVal here. ... } @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "businessService()", throwing = "ex") public void doAfterThrowingTask(Exception ex) { // you can intercept thrown exception here. ... } @Around("businessService()") public void doAroundTask(){ ... }
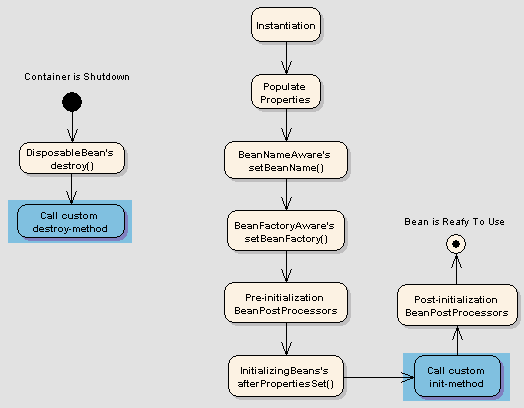
Bean Life cycel:------------InstantiationsetterConstructorAwareInterfacePostProcessBeforeInitInit methodPstProcessAfterInitDestroy(shutDownhook)
web.xml -> Dispatcher servlet -> applicationContex.xml
Dispatcher Servlet:How to change dispatcher servlet nameweb.xml: /WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet-context.xml (contains all bean details)<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher-servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>

Annotatiion:public class AppInitializer extends //web.xml AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
//applicatin-contex.xml@Configuration@EnableWebMvc@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.howtodoinjava.demo.spring"})public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Bean public InternalResourceViewResolver resolver() { InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); resolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class); resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/"); resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
java 8:1. functional interfaces and lambda expressions
has basctract mehtoda and implemnts of mehtods of ineters face can do
with the lambda expressions we can fileter the collections data with condtions
2. date time api there is no stardr api pro
3.stream api with this we can fileer the collection data
4. forEach can be used to interate the collections data
5. default and static methods implementsation inside interface
6 java 9- private methods in interface
No comments:
Post a Comment